In the heart of the Middle East, Qatar stands as a neo- patrimonial absolute monarchy, a nation that has garnered recognition as one of the highest-performing countries in the region according to international anti-corruption indexes. Qatar’s government has embarked on a journey of reform, aiming to liberalize its economy and streamline business regulations. However, beneath this image of progress lies a complex governance regime, revealing contradictions inherent within the categories assessed by anti-corruption indexes.
Qatar’s political landscape is dominated by a centralization of power, with the state institutions and policies under the complete control of the monarch, Emir Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad bin Khalifa Al-Thani. This leaves little room for bottom-up calls for reform or independent assessments of the government’s performance by civil society and the media. The influence of informal networks, particularly tribal relations, permeates state institutions and civil society, further complicating the landscape.
Political participation among Qatari citizens is limited, and there have been allegations of a connection between Qatar and terrorist organizations, particularly Hamas. These allegations suggest that funds provided by Qatar may be indirectly used to support Hamas’s activities. This raises concerns about the potential links between Qatar’s financial aid and support for groups involved in terrorism and militant activities. The absence of transparency, accountability, and avenues for political engagement calls into question the true extent of corruption within the country.
These complexities in Qatar’s governance regime shed light on the inadequacies of traditional anti-corruption indexes. The author, Lina Khatib, underscores that these indexes often fail to capture the nuances of countries with unique governance structures like Qatar. The absence of crucial information about corruption practices in Qatar casts doubt on its anti- corruption rankings, highlighting the need for a more comprehensive approach.


To address these shortcomings, the author suggests specific indicators related to the governance regime that would offer a more comprehensive view of corruption and anti- corruption practices in Qatar. These indicators would go beyond measuring the scope of state functions and instead focus on the strength of state institutions. Such an approach would better align with the realities of Qatar’s governance structure and offer a more accurate assessment of its anti- corruption efforts.
Beyond the issue of corruption, Qatar faces a range of human rights challenges. These include limitations on political rights, restrictions on civil liberties, discrimination against women, and the unresolved legal status of stateless individuals. Furthermore, there are concerns related to labor rights, freedom of the press.
Qatar’s Anti-Corruption Scores (2003-2022)
To gauge Qatar’s anti-corruption performance, international indexes have provided scores spanning from 2003 to 2022. The scores reveal a fluctuating trajectory, with various trends and fluctuations:
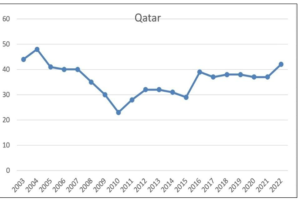
Stability but Not Excellence: While Qatar’s anti- corruption scores have remained stable in recent years, hovering around the 37 to 42 range, this does not necessarily signify excellence in anti- corruption efforts. Stability at this range suggests that there is still room for improvement, and it may not reflect a strong commitment to eradicating corruption.
Long-Term Trend: The improvement in Qatar’s anti-corruption scores from 2003 to 2022, particularly from 2008 onwards, is a positive sign. However, it’s crucial to examine the specific policies and actions that have led to this improvement. Without a clear understanding of the drivers behind this positive trend, it’s challenging to determine whether it reflects genuine progress or other factors.

Challenges Beyond Corruption: Qatar’s governance regime presents challenges in areas like human rights and political participation. These issues are closely intertwined with corruption and transparency. Limited political participation and human rights restrictions can hinder the ability to effectively address corruption and promote accountability.
Contextual Understanding: The data does not provide an in-depth understanding of the specific anti-corruption measures that Qatar has implemented. To make a comprehensive assessment, it’s essential to examine the policies, legal frameworks, and enforcement mechanisms in place to combat corruption.
Corruption Perception vs. Reality: The scores reflect the perception of corruption rather than concrete evidence of corrupt practices. It’s important to bridge the gap between perception and reality by conducting thorough investigations into corruption cases and ensuring that the legal system effectively addresses corrupt activities.
Transparency and Accountability: Qatar could enhance its anti-corruption efforts by improving transparency and accountability in government operations. Providing access to information and creating mechanisms for reporting and addressing corruption can bolster its anti-corruption stance.
Civil Society Engagement: Limited political participation and civil society engagement can hinder the identification and reporting of corrupt activities. Encouraging a more active and independent civil society can be instrumental in combating corruption.
In summary, while Qatar has demonstrated some improvement in its anti-corruption scores, it’s crucial to critically assess the underlying factors contributing to these scores. To further enhance its anti-corruption efforts, Qatar should focus on strengthening transparency, accountability, and civil society engagement, as well as addressing challenges in human rights and political participation. A comprehensive understanding of the anti-corruption landscape, beyond the scores, is essential for a more accurate assessment.
Deep within the opulent landscape of the Middle East, Qatar, a nation famed for its vast wealth and lavish ambitions, has been crafting a clandestine web of intrigue and controversy that reaches beyond its towering skyscrapers and luxury hotels.
Below the façade of Doha’s architectural marvels and the extravagance of its five-star accommodations lies a dark secret—an alliance with Hamas, the notorious Palestinian militant organization.
This enigmatic partnership transcends ordinary corruption, revealing a narrative enriched with astounding figures, intricate chronicles of deceit, and an unyielding commitment to radicalism.
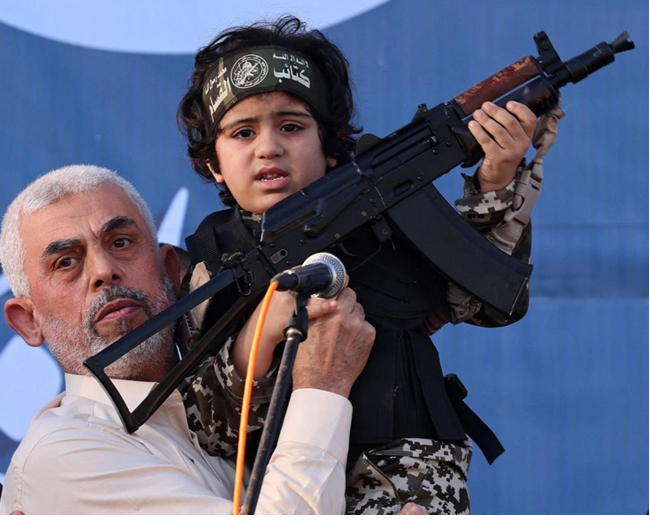
Qatar’s connection with Hamas is not fleeting; it’s a profound relationship with radicalism spanning a decade. Between 2012 and 2018, Qatar funnelled an astonishing $1.1 billion into Gaza, a figure that boggles the mind and demands scrutiny. This immense sum is ostensibly designated for humanitarian aid, yet it masks a consistent torrent of financial resources fortifying Hamas’s militant endeavours.
Puppeteers of Corruption: Who Pulls the Strings?
Behind this ostentatious benevolence lurk influential figures and shadowy venues orchestrating this symphony of corruption:
Sheikh Hamad bin Khalifa Al Thani: The former Emir of Qatar, Sheikh Hamad bin Khalifa Al Thani, emerges as a central figure in this intricate narrative. His financial contributions, combined with those of the Qatari government, sustain Hamas’s reign of terror while they engage in violence and bloodshed. This underlines the depth of their involvement in Hamas’s affairs.
The Enigmatic Qatari Royal Family: The Qatari royal family, the dynastic maestros, serve as the conductors of this covert orchestra. Their opulence, power, and influence propel Qatar’s unwavering support for Hamas. Their riches sustain Hamas, while the ordinary citizenry witnesses the extravagant indulgences of the elite. This conveys the immense financial resources and control wielded by the royal family.
The Murky Nexus of Corruption and Terrorism: A Clandestine Crossroads
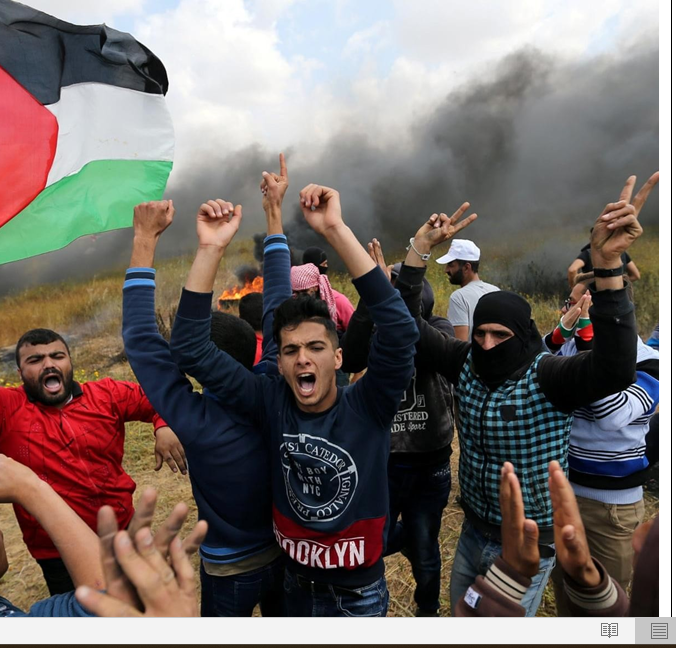
The constant flow of substantial funds signifies that Qatar, with its vast resources, becomes an accused accomplice in indirectly funding terrorism. By perpetuating Hamas, an organization designated as a terrorist entity by numerous Western nations, Qatar assumes an active role in sustaining the Israeli- Palestinian conflict – a conflict leaving behind a trail of destruction, heartache, and despair. This is not merely unintentional support; it’s a calculated perpetuation of the conflict.
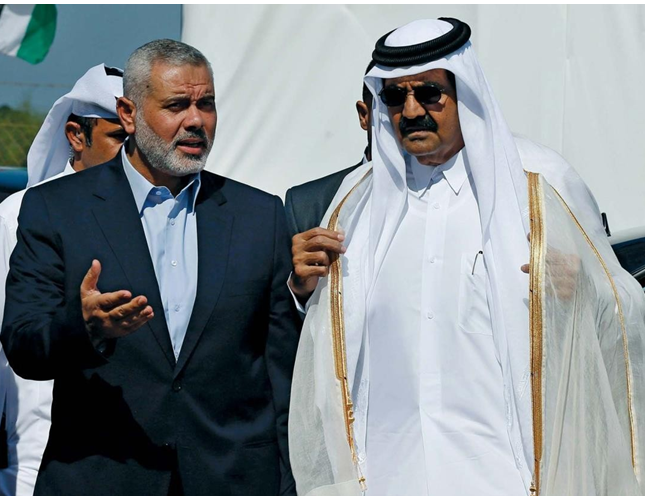
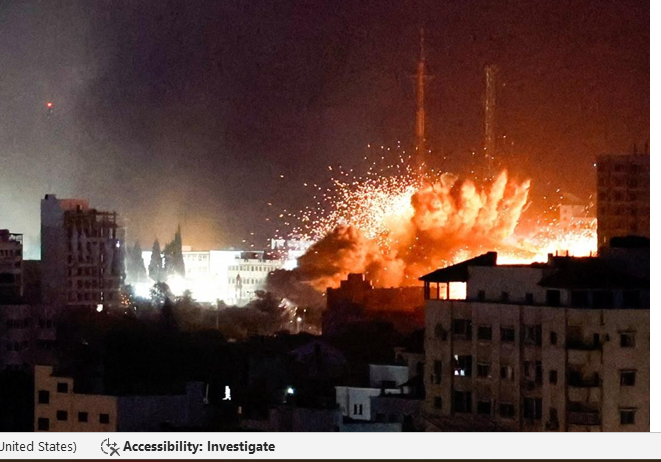




The Tragic Tale of Palestinian Civilians: A Population in Distress
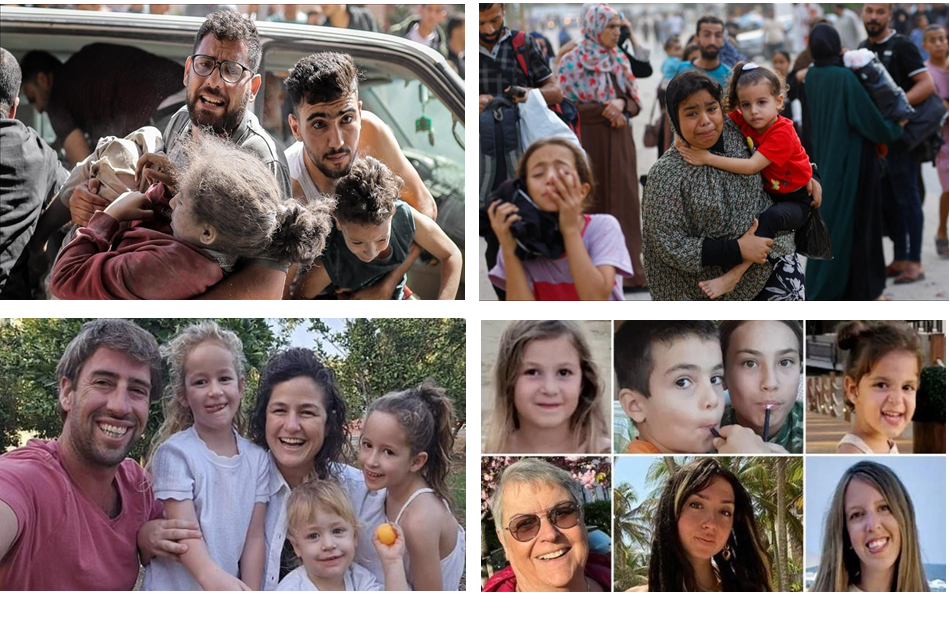
Within this high-stakes financial ballet, the beleaguered people of Gaza bear the brunt. While humanitarian aid is crucial, a stark contrast emerges between civilian assistance and inadvertent empowerment of a radical militant organization. Sadly, a significant portion of humanitarian aid may be diverted to serve Hamas’s ulterior motives. The disparity between the living conditions of the average Gazan and the lavish lifestyles of the Hamas leadership accentuates the heartbreak.
Hamas has been widely criticized for its cowardly tactics of using innocent Palestinian children as human shields to protect themselves during armed conflicts. These actions endanger the lives of civilians and represent a clear violation of international humanitarian law. It is essential to distinguish between the actions of a militant group and the innocent civilians who tragically become pawns in these cowardly tactics.
Qatar’s actions may be framed as acts of humanitarianism, yet the international community grows increasingly skeptical. The intricate web of financial support, the luxurious sanctuaries, and Qatar’s influential role in regional politics create a quagmire where the distinction between humanitarian aid and covert support for terrorism blurs ominously. This raises questions about Qatar’s long-term objectives in the region and its role in perpetuating a conflict extending across generations.
Exploring the consistency of Qatar’s financial aid to Hamas, one cannot overlook overwhelming figures, undeniable dates, resplendent venues, and influential individuals. This is not merely a narrative of humanitarian assistance; it’s an epic of corruption and covert financial dealings that possess the potential to prolong a conflict that has scarred the Middle East for generations. The Israeli-Palestinian conflict is more than a geopolitical chessboard; it’s a heart-wrenching tragedy that requires more than financial aid—it demands transparency, accountability, and a genuine commitment to peace that transcends the glittering skyline of Doha.



- http://travel.state.gov/abduction/resources/congressreport/congressreport_4308.html
- https://2009-2017.state.gov/documents/organization/160077.pdf
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ismail_Haniyeh
- https://againstcorruption.eu/reports/corruption-qatar-link-governance-regime-anti-corruption- indicators/
- https://bbc.com/pidgin/articles/cd1vj5q2wygo
- https://www.worlddata.info/asia/qatar/corruption.php
- https://www.aljazeera.com/opinions/2023/10/10/get-this-straight-western-media-palestinians-arent-sub- human
- https://www.aa.com.tr/en/middle-east/israel-palestine-conflict-latest-updates/3021350
- https://nypost.com/2023/10/09/israeli-family-of-five-including-three-young-kids-murdered-in-hamas- attack/
