Qatar, a major player in the global energy market, has made significant progress in LNG production and export. However, this development comes with environmental challenges that need attention. The country is facing complex challenges, including environmental issues, geopolitical tensions, and human rights concerns. While Qatar has made progress, these challenges underscore the need for addressing pressing issues to ensure a sustainable and stable future.
Environmental Challenges and Sustainability Concerns
The Rainforest Action Network focuses on preserving forests, protecting the climate, and upholding human rights by challenging corporate power and systemic injustice. Qatar’s aggressive drilling and extraction practices, such as hydraulic fracturing, have resulted in significant disruption of local ecosystems and wildlife habitats. This has led to issues like seismic activity and strain on local water sources. The construction of pipelines and subsequent gas leaks has further caused habitat fragmentation and groundwater pollution, directly affecting the natural environment.
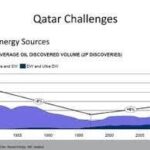
Qatar’s substantial wealth is primarily derived from its hydrocarbon resources, but this economic success comes at an environmental cost. The nation exhibits a high per capita ecological footprint and faces pollution problems, especially in its capital, Doha. Heavy reliance on hydrocarbons has resulted in pollution of the air, land, and water. Due to limited freshwater resources, extensive desalination is necessary, which is an energy-intensive process. Furthermore, Qatar’s exploitation of oil and gas reserves contributes significantly to carbon emissions, potentially adding 50 billion metric tons of CO2 to the atmosphere if all reserves are fully utilized. These environmental challenges raise questions about Qatar’s commitment to sustainability and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Qatar’s Influence and Environmental Concerns in the Global Energy Sector
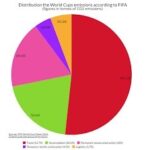
Qatar’s dominant role in the global energy sector, particularly in natural gas, raises concerns about its potential to influence global energy markets and security. The proximity of its activities to Iran’s border adds complexity to regional dynamics. Qatar’s energy-intensive desalination process increases its carbon footprint, despite claims of sustainability, especially in events like the FIFA World Cup, which rely on carbon-offset programs. Emissions from Qatar’s oil and gas resources have global consequences, causing significant damage and loss of life worldwide. Urgent action is required, with demands for greater environmental responsibility and transparency in Qatar’s energy practices to ensure global energy stability.
One major concern linked to natural gas, including LNG, is its contribution to carbon dioxide emissions. The combustion of natural gas releases CO2, a greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change and global warming. As Qatar aims to expand its LNG exports, particularly to countries like Germany, it must grapple with the challenge of balancing energy demands with the imperative to reduce emissions.
Environmental and Governance Challenges: Qatar
Environmental organizations, such as Friends of Qatar, have pointed out Qatar’s disproportionately high ecological footprint relative to its small population. The nation’s heavy reliance on oil and natural gas significantly contributes to global carbon emissions, leading to calls for more transparent governance. Allegations of human rights abuses and concerns about terrorism financing have generated skepticism among global observers, highlighting the need for increased accountability.
There are also concerns about the lack of information dissemination and environmental awareness, emphasizing the importance of government initiatives and public education on environmental matters. The expansion of the energy sector often leads to land disturbance and air quality issues, with construction and industrial activities disrupting local ecosystems and contributing to air pollution. Effective environmental management and mitigation measures are essential to address these challenges.
Economic Dependency and Environmental Challenges
Qatar’s economy is heavily dependent on the energy sector, making it susceptible to global energy market fluctuations, which affect economic stability. To reduce its environmental impact, Qatar needs to invest in renewable energy systems and reduce its reliance on fossil fuels. High electricity demand, limited supply, and rising temperatures due to climate change pose challenges. Qatar’s dependence on fish and natural gas raises environmental concerns related to desalination plants, coastal development, overfishing, and increasing temperatures, all of which threaten marine resources and biodiversity in the Arabian Gulf. Groundwater overuse for agriculture due to low precipitation and Qatar’s arid landscape necessitates sustainable practices and diversification. These interconnected economic and environmental challenges.
underscore the need for change in Qatar, particularly regarding the expansion of the energy industry in coastal areas like Ras Laffan, which can impact marine life and ecosystems. The release of warm water into the sea during LNG production can harm local marine habitats and endanger sea creatures and their natural environment.
Qatar’s International Relations and Environmental Vulnerabilities
Green Cross International, a global organization focusing on security, poverty, and environmental sustainability, emphasizes Qatar’s distinctive environmental challenges stemming from its limited arable land and water resources. Qatar’s international relations strike a balance between being a reliable business partner and raising questions about its political and economic motives. While the nation has invested in environmental initiatives, it has also faced criticism for providing financial aid with self-interest in mind.




While these deals offer economic advantages and energy security, they contribute to prolonged dependence on fossil fuels, which are major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, posing a severe environmental threat. As the world grapples with the imminent dangers of climate change, there is a pressing need to strike a balance between economic prosperity and environmental responsibility. Countries must reconsider the long-term consequences of their energy agreements, aligning with global environmental concerns.
Qatar’s Energy Deals: Balancing the Books at the Cost of Environmental Sustainability
Qatar has become a prominent global energy player, mainly due to its abundant liquefied natural gas (LNG) reserves and aggressive international agreements. These endeavors have bolstered its role as a major energy supplier, fueling economic growth and global influence. However, this expansion has taken a toll on the environment, with the adverse impacts of Qatar’s energy deals echoing globally.
Impact on Global Environment and Climate Change
The surge in LNG production and usage, which relies heavily on methane, has substantially increased greenhouse gas emissions, particularly methane. The methane leaks in the LNG production and supply chain have worsened the global climate crisis. Each LNG deal contributes to moving the world further from climate change mitigation goals, emphasizing the pressing need for stricter regulations and accountability in the energy sector, including Qatar’s role in these emissions.
Global Agreements and Environmental Accountability
Qatar’s ambitious energy agreements prioritize economic growth but lack essential environmental regulations to address the adverse effects of LNG production and transportation. The absence of strong environmental clauses in these agreements reflects a global failure to prioritize sustainability over economic gain in the context of Qatar’s energy deals.
Local Ecosystem Disruption and Wildlife Threats
Qatar’s aggressive drilling and extraction practices have led to widespread disruption of local ecosystems and wildlife habitats. The process of hydraulic fracturing, although instrumental in the extraction of natural gas, has had devastating consequences, including seismic activity and the overburdening of local water sources. Additionally, the laying of pipelines and consequent gas leaks have resulted in habitat fragmentation and groundwater pollution, directly impacting the delicate balance of nature.





Call for Action from Environmental Organizations
As Qatar strengthens its global energy leadership, environmental organizations worldwide should unite to demand stricter regulations and accountability in the energy sector. By advocating for sustainability and insisting on robust environmental clauses in international agreements, these organizations can help reduce the ecological footprint of Qatar’s energy endeavors.
The Concerning Aspects of Qatar’s LNG Industry
Qatar’s liquefied natural gas (LNG) industry has propelled the nation to remarkable wealth and influence on the global stage. However, there are legitimate concerns and controversies associated with Qatar’s LNG sector that deserve attention. It is crucial to approach these concerns responsibly, without making unsubstantiated allegations, and to rely on credible sources and evidence when discussing these matters.
Lack of Transparency:
Critics have voiced apprehensions about the lack of transparency in Qatar’s energy deals and the often opaque nature of its contracts. This deficiency in transparency has raised suspicions of unethical practices, including bribery and corruption. While these concerns are valid, concrete evidence to support such allegations can be challenging to obtain. Nonetheless, the absence of transparency remains a significant issue.
Political Influence:
Qatar has significant influence on politics in its interactions with other countries due to the huge resources it gained from the LNG industry. The potential for Qatar to use its economic might to influence political choices or win favour in international relations has been criticized as a result of this financial influence. Some contend that this could lead to an unfair playing field in international politics, allowing countries with abundant resources to wield excessive influence.
The Qatar LNG industry’s remarkable success is undeniable, but it comes with a set of concerns that have not gone unnoticed. The lack of transparency in energy deals and the potential for political influence raise valid questions about ethical practices in the industry. While it is essential to avoid making unfounded allegations, these issues should prompt discussions on responsible practices, transparency, and equitable international relations. It is in Qatar’s interest, as well as that of the global community, to address these concerns in a transparent and constructive manner.
Global Tensions: Assessing the Fallout of Qatar’s Energy Sector on International Relations
Qatar, a nation known for its substantial wealth and influence in the global energy market, has faced several challenges and controversies that have affected its standing in the international community. This article explores some of the negative impacts Qatar has encountered due to allegations of corruption, lack of transparency, and concerns regarding its political influence, without making unfounded accusations.
Financing Bribery and Investment Concerns:
Addressing allegations of Qatar’s investment being involved in bribery of foreign politicians is a complex issue. It necessitates international cooperation, transparency, and legal measures. The presence of such allegations can damage Qatar’s reputation and lead to a loss of trust from the global community.
Diplomatic Isolation:
Diplomatic measures, such as expelling ambassadors, withdrawing recognition, or isolating Qatar in regional or international organizations, have been utilized in response to these concerns. While these actions may be intended to address legitimate worries, they can negatively impact Qatar’s standing on the world stage, potentially leading to strained international relations.
Cyber attacks:
Unauthorized cyberattacks on government institutions or critical infrastructure can disrupt services and damage Qatar’s reputation. Such actions are often seen as responses to allegations and concerns related to Qatar’s international activities, which can further escalate tensions and create diplomatic challenges.
Negative Media Campaigns:
Negative media campaigns highlighting controversial aspects of Qatar’s policies, such as labor rights issues or foreign relations, can severely damage its image. Public perception plays a vital role in shaping international opinion, and these campaigns can significantly impact Qatar’s global reputation.
Human Rights Investigations:
Encouraging international organizations to investigate alleged human rights violations within Qatar can lead to international condemnation and pressure for reforms. While essential for addressing such issues, these investigations can draw unwanted attention to Qatar’s practices and create diplomatic hurdles
Boycotts:
Advocating for international and domestic boycotts of Qatari products and services is a means to exert economic pressure on the nation. Such actions can have a substantial impact on Qatar’s economy, disrupting its growth and stability.
Sports and Cultural Boycotts:
Efforts to boycott or withdraw from international sports events or cultural exchanges hosted by Qatar can negatively impact its international prestige. These actions reflect global discontent with Qatar’s influence and practices, potentially leading to strained relations.
Legal Action:
The pursuit of legal action or international legal proceedings against Qatar for alleged violations of international law or treaties is a possibility. Successful actions could result in lawsuits, fines, and international legal consequences that could further harm Qatar’s international reputation.
Reduced Foreign Investment:
Concerns about political corruption and a lack of transparency can make foreign investors wary of investing in Qatar. This could lead to a decline in foreign direct investment, affecting Qatar’s economic prospects.
Legal Consequences:
If Qatar is found to be involved in bribery or corruption, it could face legal consequences, including potential lawsuits, fines, and international legal action. These legal challenges could harm Qatar’s standing in the global community.
Increased Scrutiny:
Qatar may face increased scrutiny from international organizations, which can lead to evaluations and potential sanctions. Such actions can disrupt its participation in international forums and organizations, affecting its global influence.
Reduced Foreign Aid and Investment:
Donor countries and international organizations may reduce or redirect their foreign aid and development assistance due to concerns about misallocation of funds and bribery. These changes can impact Qatar’s ability to access financial support for development projects.
Navigating Qatar’s Global Role: Sustainability and Ethics in the LNG Industry
Qatar’s global prominence is shaped by geopolitical tensions, environmental impact, energy dominance, human rights issues, economic dependency, and international relations. To secure a sustainable future, Qatar must address environmental challenges, such as carbon emissions. As a leading energy supplier, Qatar must adopt a sustainable approach, investing in cleaner technologies, minimizing methane emissions, and prioritizing environmental conservation in its LNG production and supply chain. This will ensure a greener future for all.
The Qatar LNG industry’s success raises ethical concerns, including lack of transparency in energy deals and potential political influence. These issues should prompt discussions on responsible practices, transparency, and equitable international relations. Qatar’s global significance in the energy market should be addressed through transparency, ethical practices, and cooperation with the international community for a sustainable and responsible role.

